If A Price Ceiling Is Not Binding
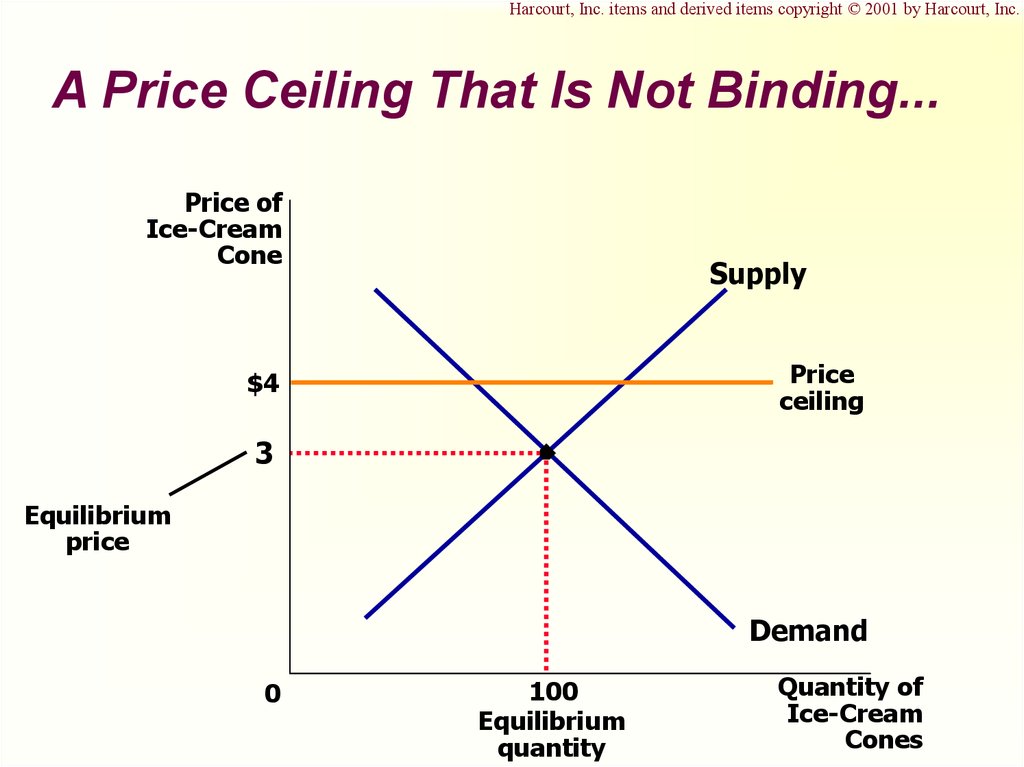
This is an example of a non binding or not effective price ceiling.
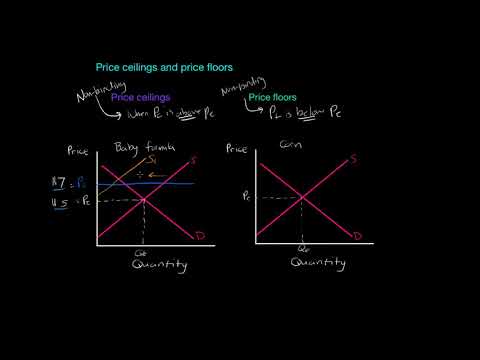
If a price ceiling is not binding. For instance if the government sets the ceiling for potatoes at 5 per pound but the equilibrium price for potatoes is already 4 per pound this would have no real effect on the price of potatoes. If the equilibrium price is already lower than the price ceiling the price ceiling is ineffective and called a non binding price ceiling. For competitive markets like the one shown above we can say that a price ceiling is non binding when pc p.
The answer is no because everyone who is willing to pay up to 2 000 gets an apartment and everyone who is willing to supply an apartment for 2 000 gets paid. However if you hit the equilibrium price first the price floor is not binding is not. A legal minimum on the price at which a good can be sold is called a price 11.
In this case the ceiling has no practical effect. There will be a shortage in the market. There will be a shortage in the market.
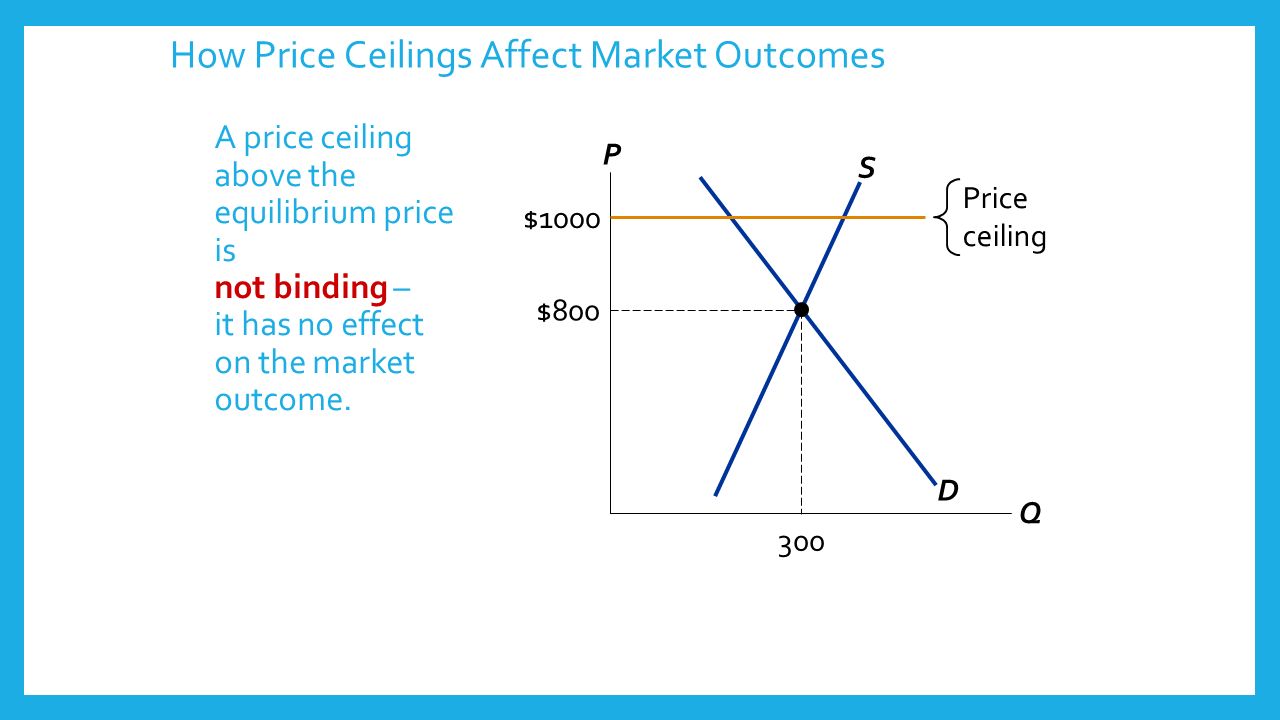
If price ceiling is set above the existing market price there is no direct effect. When price ceiling is set below the market price producers will begin to slow or stop their production process causing less supply of commodity in the market. If a price ceiling is not binding then a.
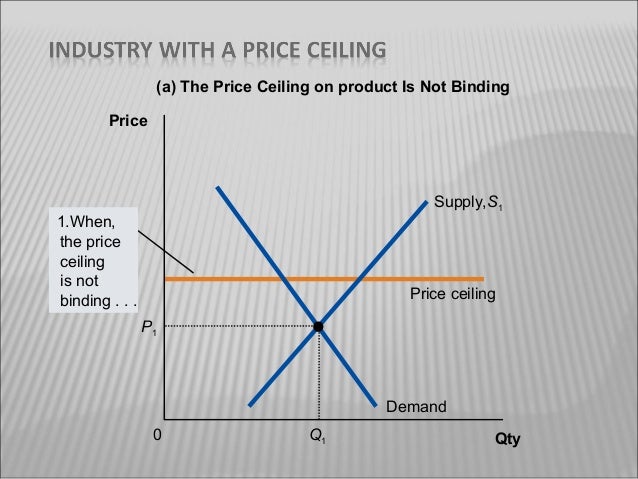
Note that the price ceiling is above the equilibrium price so that anything price below the ceiling is feasible. If a price ceiling is not binding then a. The market will be less efficient than it would be without the price ceiling.
Another way to think about this is to start at a price of 100 and go down until you the price floor price or the equilibrium price. The market will be less efficient than it would be without the price ceiling. For example suppose that the prevailing equilibrium price was 100 still and the government set the price ceiling to be 130 the price would still be 100 not 130.